Enhancing Lithium-Ion Battery Technology: Strategies for Improving Energy Density and Performance
With the increasing demand for lithium-ion batteries, high energy density and high power density lithium-ion battery technology has become one of the research hotspots. Increasing electrode thickness, material modification and development of new materials can effectively improve the energy density of the battery, while the electrode microstructure parameters such as porosity, pore size and distribution, and curvature of the electrode are the key factors determining the performance of the electrode and the battery.
Analyzing Pore Characteristics of Lithium-Ion Porous Electrodes: Methods and Significance
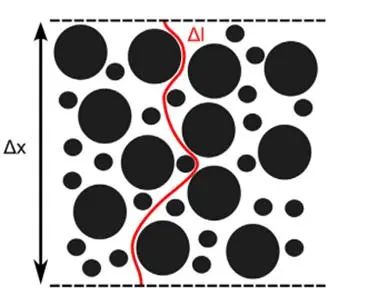
From the current research of lithium-ion porous electrodes, it can be found that the actual porous electrode pores are affected by the accumulation effect and filling effect of particles, and the pore size and distribution are not uniform, and the zigzag degree is difficult to characterize. In order to characterize the pore characteristics of porous electrodes, researchers have devoted themselves to the development of efficient and fast methods for measuring the zigzag degree, such as the gas transmission resistance measurement method , the heat exchange method for hydrodynamic simulation of porous electrodes, the FIB-SEM reconstruction of 3D electrode structure measurement method, and the symmetric battery electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) test method. Among them, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy is easy to operate, and the test time is short. Because the electron transmission resistance of lithium-ion porous electrodes is usually small, the true curvature of porous electrodes can be obtained by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. In addition, the measurement method of symmetrical battery electrochemical impedance spectroscopy can also be used to analyze the electrolyte wettability and the membrane curvature of the electrode plate, and has a certain guiding significance for the judgment of the production line electrolyte wettability time.Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) was used to measure symmetrical cells assembled with negative electrode plates of different compaction. The ion resistance of each pole piece was obtained by fitting the EIS spectrum, and then the ion resistance value was substituted into the formula to obtain the McMullin number of the pole piece, as shown in Figure 5. It can be seen from the trend of the data that the ion resistance and McMullin number increase with the increase of the compaction density of the electrode sheet, indicating that the curvature of the graphite negative electrode sheet increases with the increase of the compaction.
Effect of Compaction Density on Electrolyte Performance and Ion Transmission in Lithium-ion Batteries
With the increase of compaction density, the contact between graphite particles and conductive particles is more dense, the performance of the absorbing electrolyte deteriorates, and the electrolyte is difficult to infiltrate, making the migration of lithium ions more difficult, increasing the ion transmission impedance, resulting in an increase in the curvature of the pole sheet.
The Impact of Electrode Compaction Density on Battery Performance
Generally speaking, within the compaction range allowed by the material, the greater the electrode compaction density and the more active material contained per unit volume, the higher the capacity of the battery can be done. However, when the compaction of the pole plate is too high, the porosity is reduced, the greater the zigzag degree, the longer the lithium ion transmission path, which will seriously reduce the magnification performance and cycle performance of the battery. Especially for thick electrodes, low curvature is one of the key factors in the design of electrode structure. Therefore, compaction density is very important for battery design. We can preliminatively characterize the magnification performance of the pole sheet in the battery by testing the curvature of the pole sheet, so as to determine the appropriate design scheme of the pole sheet.