The Role of Conductive Agents in Enhancing Lithium-Ion Battery Conductivity
Lithium-ion batteries are constructed from essential raw materials such as positive and negative electrode powders, separators, electrolytes, conductive agents, binders, and current collectors. The efficient manufacture of these batteries requires processing under optimal conditions tailored to these materials. Any change in raw material parameters necessitates adjustments in the process to achieve superior electrical performance.
Importance of Conductive Agents in Electrode Design
In lithium-ion battery technology, the design of positive and negative electrode plates is crucial. This involves decisions on parameters like loading of active material, porosity, thickness, and proportioning of active material, conductive agent, and binder. Conductive agents are pivotal as they facilitate electron transfer during charging and discharging. Their content and performance significantly impact electron movement, thereby determining the overall electrochemical quality. The electronic conductivity path, often relying on the conductive agent, underscores the need for optimal conductive pathways especially since active materials alone may exhibit poor conductivity.
Testing Methods for Conductive Agents
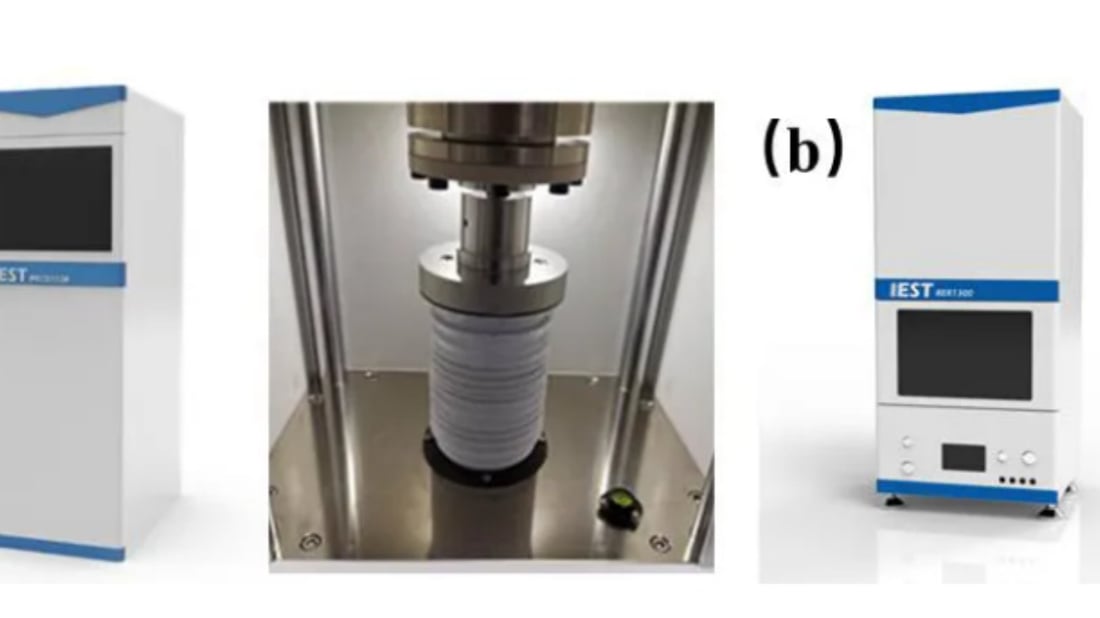
The PRCD3100 series powder resistance meter and BER2500 series pole piece resistance tester, both from IEST Yuanneng Technology, are used to assess the conductivity of powder materials and pole pieces. Sample preparation involves testing different NCM ratios with conductive agents, and evaluating resistance in powders under varying pressures.
Impact of Conductive Agents on Test Results
Conductive agent SP drastically improves the conductivity of mixed powders containing NCM, PVDF, and other variants, as demonstrated by testing results showing enhanced conductivity paths. Poorly conductive binders like PVDF can decrease conductivity by reducing particle contact, whereas a well-chosen conductive agent enhances electron transfer. Adjusting the conductive agent content optimizes performance, improving electron pathways across different pressures, thus highlighting its importance at both powder and electrode levels.
Conductive Agent Optimization in Slurry and Electrodes
Preparation based on specific ratios tested through manual coating of slurries showed notable variances in electrode conductivity, matching the trends observed in powder tests. Conductive agents play a crucial role at both the powder level and electrode level, highlighting the necessity for proper ratio optimization, which hinges on factors such as active material particle size and specific surface area. The percolation theory model guides systematic experimentation to determine the best conductive agent blend.
Conclusion on Conductive Agents' Role
By employing the PRCD series for powder resistance and the BER series for pole plate resistance evaluation, the role and impact of conductive agents are thoroughly examined. This research bridges powder and electrode levels, offering insights that enable further electrode formulation improvements. Understanding conductive agent effects helps predict electrode performance from powder characteristics, aiding in advancing lithium-ion battery technology.