The Process of Lithium Battery Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Guide
In the ever-evolving world of technology, the process of lithium battery manufacturing continuously adapts with new methods and innovations. Here, we explore the detailed steps involved in creating lithium batteries.
Overview of 13 Key Steps in The Process of Lithium Battery Manufacturing
The production of lithium batteries is divided into 13 essential steps: positive electrode batching, negative electrode batching, coating, positive electrode preparation, negative electrode preparation, winding, shelling, rolling groove, cell baking, liquid injection, and super-welding cap.
1. Positive Electrode Batching
In the process of lithium battery manufacturing, the positive electrode involves a blend of active substances, a conductive agent, and a binder. Key factors include temperature and stirring speed, which are crucial for the internal resistance and electrical performance of the battery.
2. Negative Electrode Batching
The negative electrode follows a similar path but requires a dispersant in addition to the main components. The aqueous mixing process emphasizes specific conditions and materials like deionized water.
3. Coating
During the process of lithium battery manufacturing, slurry is extruded or sprayed onto the current collectors. The temperature and specific density needs are meticulously controlled to avoid defects.
4. Positive Electrode Preparation
After drying the coated cathode, compression serves to compact the pole piece. Options such as hot pressing and cold pressing offer different advantages in terms of compaction and rebound.
5. Negative Electrode Preparation
Following similar steps as the positive electrode, the negative electrode preparation focuses on ensuring no surface defects and an optimal alignment during manufacturing.
6. Preparation of Positive Electrode Piece
Post-slitting, the positive electrode undergoes drying and encapsulation processes. Tab considerations include length and compatibility to prevent short circuits and facilitate welding.
7. Preparation of Negative Electrode Piece
This stage involves drying and welding of the negative electrode similar to its positive counterpart, with added emphasis on tab length and encapsulation.
8. Winding
Winding integrates the diaphragm and both electrode pieces into a single core. Here, the control of tension and alignment becomes pivotal in the process of lithium battery manufacturing.
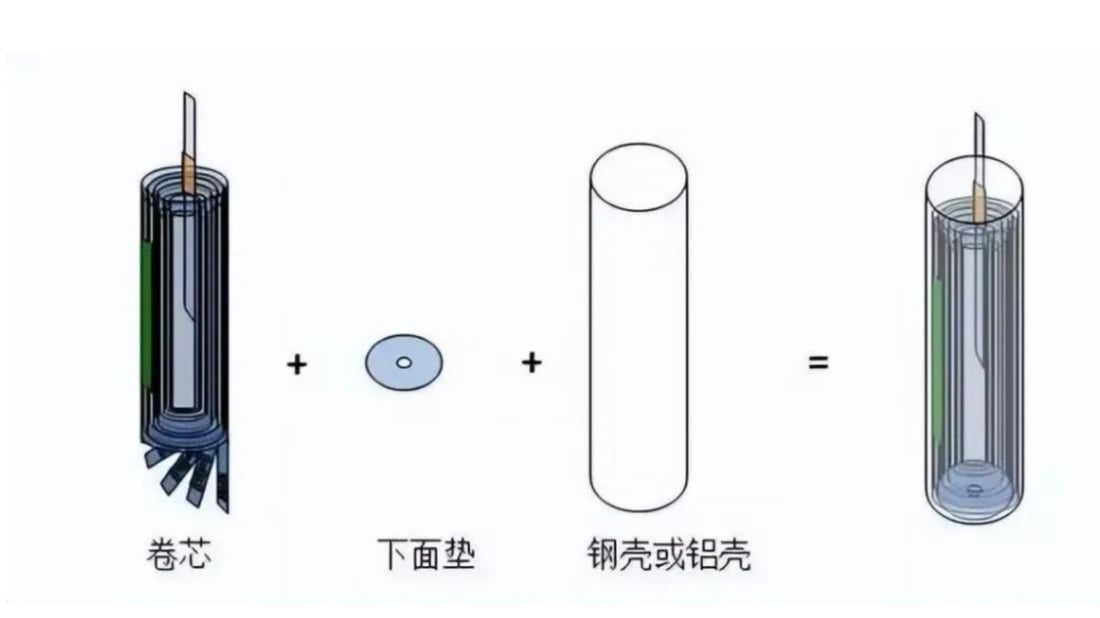
9. Inserting into the Shell
The core is subjected to tests and inserted into a shell, focusing on controlling moisture, burr, and dust, which are critical factors throughout the process of lithium battery manufacturing.
10. Rolling Grooves
Rolling grooves secure the core within the shell without causing damage. This requires precision in balancing the speeds of transverse extrusion and longitudinal pressure.
11. Cell Baking
Baking is crucial to reduce moisture content, using a vacuum oven to ensure optimal performance and safety in the final battery cells.
12. Electrolyte Injection
Electrolyte injection follows, using precise measurements and vacuum conditions to facilitate thorough absorption into the electrode pieces.
13. Super-Welding Caps
The final step in the process of lithium battery manufacturing involves super-welding caps. This requires careful alignment and testing to ensure a secure fit and function.
Conclusion
The intricacies of the process of lithium battery manufacturing demand a high degree of precision and control, embracing innovation at every stage to improve performance and safety.