Understanding Internal Resistance in Lithium-ion batteries
The Importance of Internal Resistance in Lithium-ion Batteries
The internal resistance of lithium-ion batteries is a vital factor in determining their overall performance. It influences key attributes like charge and discharge efficiency, power output, thermal management, and aging rate.
Methods for Measuring Internal Resistance in Lithium-ion Batteries
Three primary methods are used to test the internal resistance of lithium-ion batteries: DC internal resistance (DCIR), AC internal resistance (ACIR), and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS).
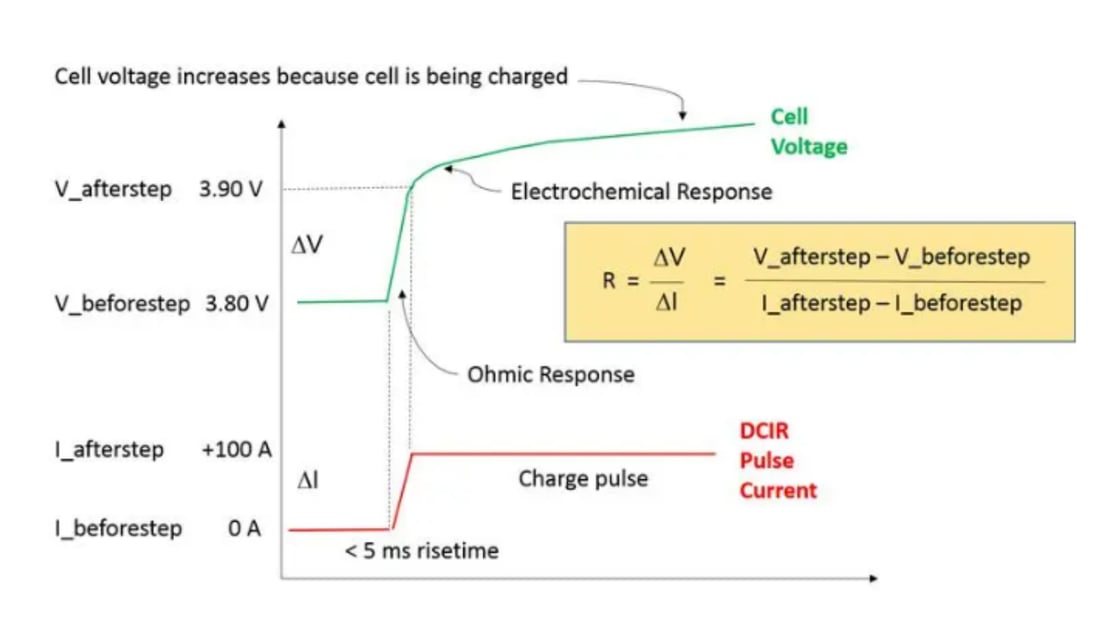
DC Internal Resistance (DCIR) in Lithium-ion Batteries
The DCIR method involves applying a small DC pulse current to lithium-ion batteries and measuring the voltage change. Using Ohm's law (V=IR), the internal resistance is calculated. This method provides a quick assessment of battery health and performance. The IEC 61960 standard suggests using discharge pulses to derive DCIR values.
AC Internal Resistance (ACIR) for Lithium-ion Batteries
ACIR tests are performed by applying a small AC signal to the lithium-ion battery and measuring the AC response. This method, typically conducted at 1 kHz, allows for the analysis of impedance without the interference from low-frequency electrochemical processes.
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy (EIS) in Lithium-ion Batteries
EIS is a more complex technique used to analyze the impedance properties of lithium-ion batteries over a range of frequencies. It provides comprehensive insight into the battery's internal electrochemical processes, making it invaluable in research and development.
Comparing DCIR and ACIR in Lithium-ion Batteries
ACIR offers fast and highly reproducible measurements and is ideal for quick battery inspections. DCIR, although less reproducible, provides a more accurate representation of a lithium-ion battery's internal resistance during real-world use.
Normalized Internal Resistance in Lithium-ion Batteries
According to manufacturer specifications, the normalized internal resistance for commercial LFP lithium-ion batteries typically ranges from 35 to 70 mΩ*Ah.