The Influence of Carbon Coated Aluminum Foil on Lithium Iron Phosphate Electrode Sheets
Lithium-ion batteries are intricate systems, comprising key components such as positive and negative electrode plates, separators, and electrolytes. Among these, electrode sheets, including lithium iron phosphate electrode sheets, are crucial in determining battery performance. During battery operation, electrons and ions traverse the electrode sheets, undergoing complex chemical and electrochemical transformations. Consequently, the conductivity of lithium iron phosphate electrode sheets and the uniformity of their conductive networks are vital in optimizing battery performance.
The Role of Aluminum Foil as a Current Collector
As an essential carrier for electrons and active materials, the current collector significantly impacts the overall performance of battery cells. Aluminum foil is predominantly used as a positive electrode current collector. To enhance the functionality of lithium iron phosphate electrode sheets, conductive coatings are applied to the aluminum foil surface, effectively reducing the interface contact resistance with active particles and strengthening the bond between the active material and the current collector. This minimizes the peeling of active particles during electrode cycling.
Benefits of Carbon Coated Aluminum Foil
Presently, carbon coated aluminum foil is primarily utilized in lithium iron phosphate electrode sheets for power batteries. This is because lithium iron phosphate's olivine crystal structure inherently has low electronic and ionic conductivity and weak adhesion to current collectors, limiting its applications. The carbon coated aluminum foil enhances the adhesion, reduces charge transfer resistance, and decreases the internal resistance of lithium iron phosphate electrode sheets, resulting in improved lithium ion diffusion rates. This ultimately boosts both the cycling and rate performance of the lithium iron phosphate electrode sheet batteries.
Research and Testing on Conductivity
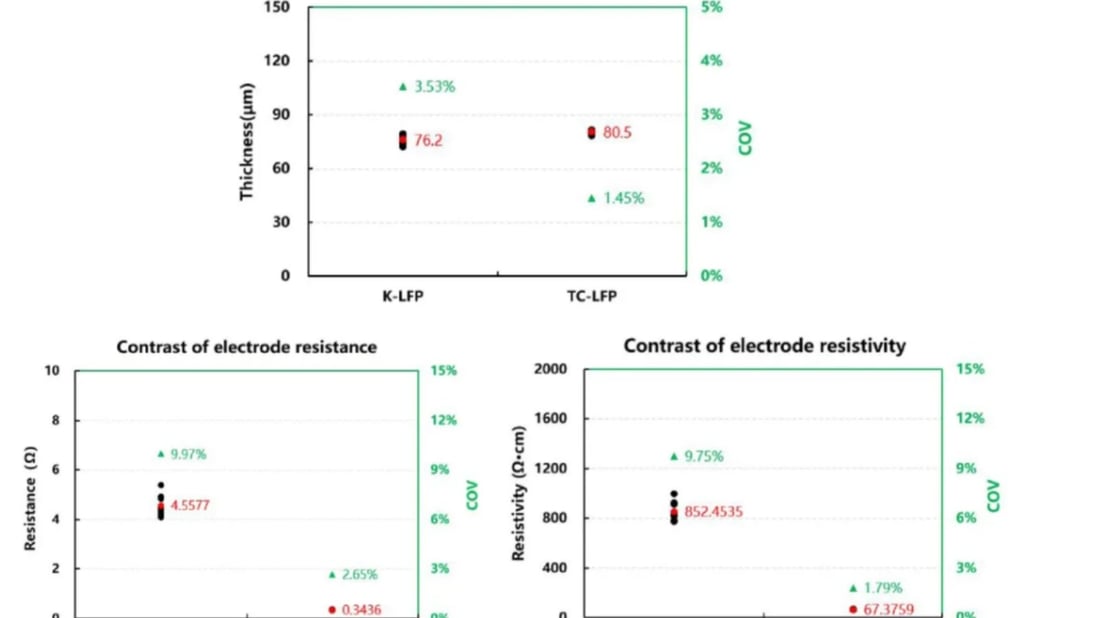
Using the BER2500 electrode resistance tester from Yuanneng Technology (Xiamen) Co., Ltd., we evaluated the electronic conductivity of plain and carbon coated aluminum foil, alongside the conductivity of lithium iron phosphate electrode sheets coated with these materials. The carbon coating's impact on electronic conductivity was evident, as it increased the resistance and resistivity but improved the consistency and uniformity of the foil's conductivity. Post lithium iron phosphate application, the resistance and resistivity notably diminished, leading to better performance in lithium iron phosphate electrode sheet batteries.
Advantages of Carbon Coating on Lithium Iron Phosphate Electrode Sheets
The integration of carbon coated aluminum foil into lithium iron phosphate electrode sheets not only enhances interfacial contact resistance but also offers synergistic benefits. A stable conductive layer serves as a diffusion barrier against oxygen from side reactions, hindering oxide layer formation on the metal current collector, thereby preventing degradation. The conductivity of the lithium iron phosphate electrode sheet is improved, facilitating rapid charge transfer and reduced interface resistance. The mechanical flexibility enhances interface adhesion, minimizing contact area loss due to stress during prolonged cycling. This innovative approach significantly upgrades the electrochemical performance, reversible capacity, capacity retention, and overall rate performance of lithium iron phosphate electrode sheets.