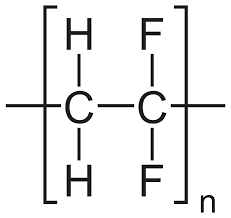
Overview: What is PVDF Polymer?
PVDF polymer, or polyvinylidene fluoride, is a type of thermoplastic fluoropolymer. It is a highly versatile polymer that has various applications in different industries. PVDF is durable, UV resistant, chemical resistant and has high-temperature tolerances.
The Materials Needed for Making PVDF Polymer
Some of the basic materials that are required to make PVDF polymer include vinylidene fluoride, a chain transfer agent, an initiator, catalyst, dispersant, stabilizer, and solvent. These materials play a significant role in the polymerization process of PVDF.
Synthesis of PVDF Polymer through the Emulsion Method
The emulsion method is one of the most popular synthetic routes for producing PVDF polymer. In this technique, vinylidene fluoride is added to an emulsion solution containing an initiator and a surfactant. The solution is then heated, and the polymerization process is initiated.
Suspension Polymerization Method for Making PVDF Polymer
This method involves the use of a suspension system where vinylidene fluoride is suspended in a liquid medium containing a stabilizer and an initiator. The solution is heated to a specific temperature under high pressure, which initiates the polymerization process of PVDF.
Steps in PVDF Polymerization
Polymerization of PVDF involves three crucial steps: initiation, propagation, and termination. During the first stage, initiation, the initiator begins to form free radicals in the polymer matrix. These free radicals then propagate to form chains that, if allowed to continue, would indefinitely grow until the monomer is depleted. The termination stage involves stopping the polymerization process before the chain becomes too large to handle.
Properties of PVDF Polymer
PVDF polymer has various unique properties, making it ideal for a broad range of applications. Some of these properties include high thermal stability, chemical resistance, excellent electrical insulation, abrasion resistance, and UV resistance.
Applications of PVDF Polymer
PVDF polymer has numerous applications in different industries, including the automotive, aerospace, chemical, electrical, and medical fields. Its most common applications include coatings, membranes, lithium-ion batteries, cables, wires, and piping.
Advantages of PVDF Polymer
PVDF polymer presents a vast array of advantages over other materials, including its high mechanical strength, superior flexibility, and resistance to UV light, harsh chemicals, and extreme temperatures.
PVDF vs. Other Polymers
Compared to other polymers, PVDF polymer is preferred for its excellent mechanical and chemical properties. For example, it has better chemical resistance than PVC, better thermal stability than PTFE (Teflon), and better impact resistance than Nylon.
Conclusion
PVDF polymer is a unique thermoplastic fluoropolymer with a vast array of applications in various industries. It is crucial to understand the process of making PVDF polymer to take advantage of its unique properties and benefits fully.
PVDF polymer, thermoplastic fluoropolymer, polymerization, synthesis, properties, applications, advantages, emulsion method, suspension method
How do you make PVDF polymer?? Benefits and Applications
Learn the synthesis process and different applications of polyvinylidene fluoride(PVDF) polymer. Discover its unique properties and advantages over other materials.
steps in PVDF polymerization, how to make PVDF polymer, advantages of PVDF polymer, PVDF vs other polymers, benefits of PVDF polymer, PVDF properties and applications
Quote Inquiry
Contact Us Now!