Revolutionizing Solid State Batteries with Solid electrolyte powder ions
Understanding Solid Electrolyte Powder Ions in Battery Technology
The pivotal variance between solid-state and liquid batteries lies in their electrolytes, where solid electrolyte powder ions play a crucial role. Liquid battery electrolytes predominantly consist of carbonate solvents combined with lithium salts. On the other hand, solid-state batteries utilize solid substances, leading to innovative battery designs.
Solid Electrolyte Powder Ions: Categories and Characteristics
Solid electrolyte powder ions are integral to ion conduction in solid-state batteries, substantially enhancing safety over traditional liquid lithium-ion batteries by eliminating PP/PE separators, which mitigates risks like lithium dendrite penetration. Key categories of solid electrolyte powder ions include oxides, sulfides, polymers, and halides.
Each category of solid electrolyte powder ions has unique attributes. Oxide solid electrolytes, noted for their hardness, often pair with liquids to form semi-solid-state batteries. Sulfides, though moisture-sensitive, are considered promising for their high conductivity and softer texture. Polymer-based solid electrolyte powder ions suffer from low conductivity, whereas halides, still in research, offer promising ionic conductivity and voltage stability.
Global Advances in Solid Electrolyte Powder Ions
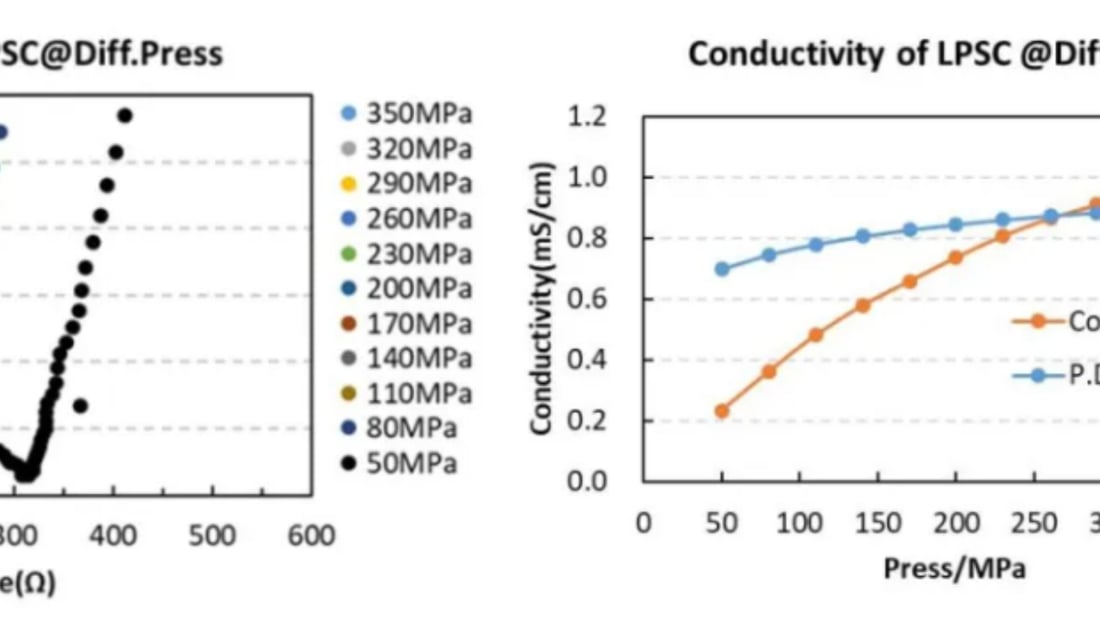
Countries like Japan and South Korea prioritize the sulfide route for developing solid electrolyte powder ions, while domestic enterprises often opt for oxides. This path enhances processing speed with semi-solid technologies. The pressure's influence on solid electrolyte powder ions’ performance can be profound, boosting ionic conductivity.
Testing Solid Electrolyte Powder Ions: The SEMS1100 System
Yuanneng Technology’s SEMS1100 system marks a breakthrough in assessing solid electrolyte powder ions. It allows real-time measurements of ionic conductivity under pressure, vital for battery development.
Solid Electrolyte Powder Ions in LPSC and LLZO
Sulfide solid electrolyte powder ions, like LPSC, exhibit impressive conductivity akin to liquid electrolytes. The SEMS1100 device reveals a decrease in EIS spectra with pressure increment, signifying better conductivity. Conversely, oxide electrolytes such as LLZO demonstrate lower conductivity due to poor particle-to-particle contact.
Challenges and Future Directions for Solid Electrolyte Powder Ions
Despite high compression generating excellent conductivity in sulfide solid electrolyte powder ions, major challenges persist, including environmental stability and interface compatibility. Yet, with continued research, the potential of solid electrolyte powder ions in revolutionizing battery technology remains promising.
Conclusion: The Future of Solid Electrolyte Powder Ions
In conclusion, while oxide solid electrolyte powder ions often require combination with polymer or liquid counterparts, sulfide forms stand out for independent high conductivity after compression. Addressing existing issues could cement the role of solid electrolyte powder ions in daily battery technology, steering towards a safer energy future.