Understanding the Diffusion Kinetics of Lithium Ion Batteries
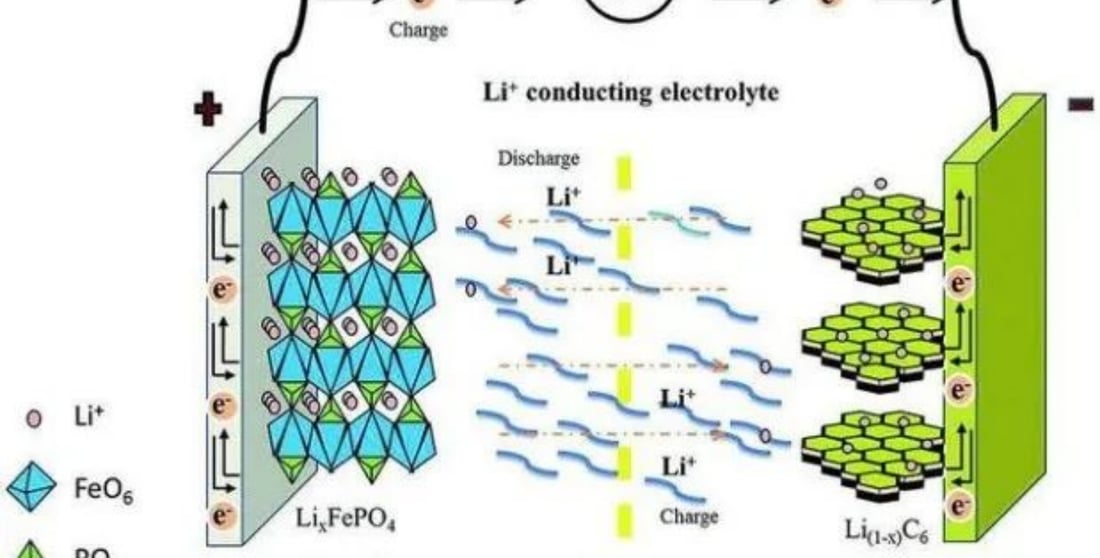
Lithium ion batteries, often used in 12 volt lithium ion battery chargers, are a type of secondary battery that operates by the movement of lithium ions between electrodes. The charging process releases lithium ions from the positive electrode, which then pass through the electrolyte and embed into the negative electrode. Simultaneously, electrons travel from the positive to the negative pole through an external circuit, creating an electric current. When discharging, lithium ions migrate from the negative electrode back to the positive, with electrons reversing their flow to generate power for external use.
The Importance of Diffusion Rate in Battery Performance
The diffusion rate of lithium ions significantly impacts the efficiency of 12 volt lithium ion battery chargers. It affects the charge/discharge speed, cycle life, and temperature performance of the battery. Therefore, understanding and measuring this diffusion rate is crucial. The Galvanostatic Intermittent Titration Technique (GITT) offers a transient measurement method that quantifies lithium ion diffusion in electrode materials through the potential-time relationship.
Pulse Constant Current Relaxation: The GITT Method
The GITT testing process involves repeated "pulse constant current relaxation" cycles. Each cycle includes applying a constant current to charge or discharge the battery for a specific duration, disconnecting the current, and recording voltage changes. Precision in maintaining constant current and accurate voltage is vital, especially when assessing 12 volt lithium ion battery chargers.
Relaxation and Diffusion Coefficients
During the relaxation phase after the current stops, lithium ions must sufficiently diffuse within the active material. The diffusion coefficient is calculated based on the voltage-time relationship, offering insights into the charger efficiency and diffusion kinetics. Conditions must ensure the diffusion primarily occurs on the solid-phase material surface. Key limitations include short pulse times (t<
Optimizing 12 Volt Lithium Ion Battery Chargers
By utilizing the GITT method, manufacturers can enhance the efficiency of 12 volt lithium ion battery chargers. Ensuring optimized diffusion kinetics allows for better performance, longer cycle life, and improved temperature resistance in lithium ion batteries. This process underlines the necessity of short pulse durations and adequate relaxation to unlock the full potential of chargers.